Cardiovascular Disease & Health
Cardiovascular Disease causes around 50,000 deaths in Australia annually and more than 17 million deaths around the world. It is the leading cause of non-communicable disease death globally.
The heart receives its blood supply from a number of large arteries, the coronary arteries. Damage to, narrowing or blockage of any of these deprives the heart of blood supply and causes the heart to malfunction.
Coronary heart disease (disease of the blood vessels of the heart) affects more than 500,000 Australians annually. In 2012 CHD was the cause of 20,000 deaths.
Atherosclerosis starts as a fatty streak in an artery, which progressively builds up lipids and causes that area of artery to narrow. A myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack) is when that part of the artery becomes completely blocked and does not allow blood flow past that point.
Risk Factors for CHD:
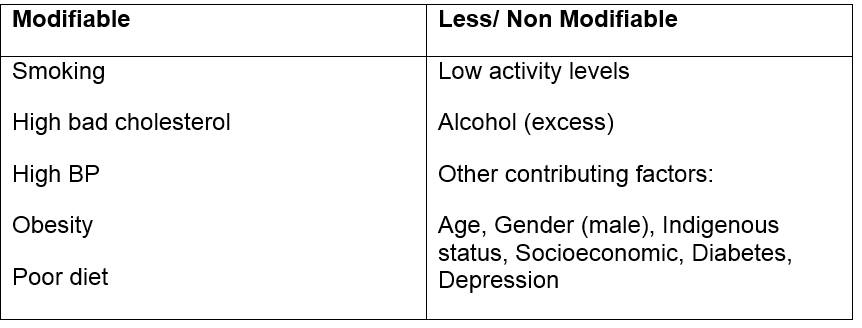
Management of CHD:
- Medications
- Percutaneous coronary intervention – insertion of a stent into the artery
- Coronary artery bypass graft
Whatever type of treatment is undertaken Cardiac Rehabilitation plays a big part in the management of the disease.
CHRONIC HEART DISEASE
The cycle of chronic heart disease becoming a chronic condition lo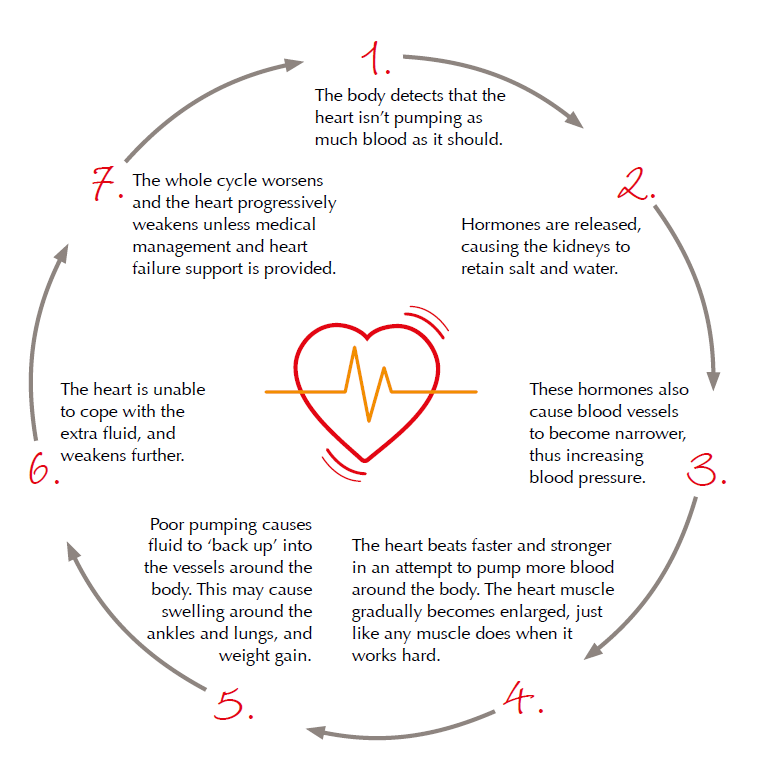
The management of Chronic Heart Failure:
- Lifestyle intervention to help get the best long term outcome and quality of life – CARDIAC REHABILITATION
- Optimal physical activity (physiotherapists can create an individualized rehab programme to work at a level that is safe but if performed regularly will help improve heart function)
- Diet is a key. A high fibre diet, small meals, controlling the type of fats eaten and limiting salt intake is recommended
- Fluid management (this is under medical advice)
- Smoking cessation
- Sleep apnoea (stopping breathing when asleep) – excessive snoring is a symptom of sleep apnea. Sleep studies can determine the level of sleep apnoea and a number of strategies can address the problem.
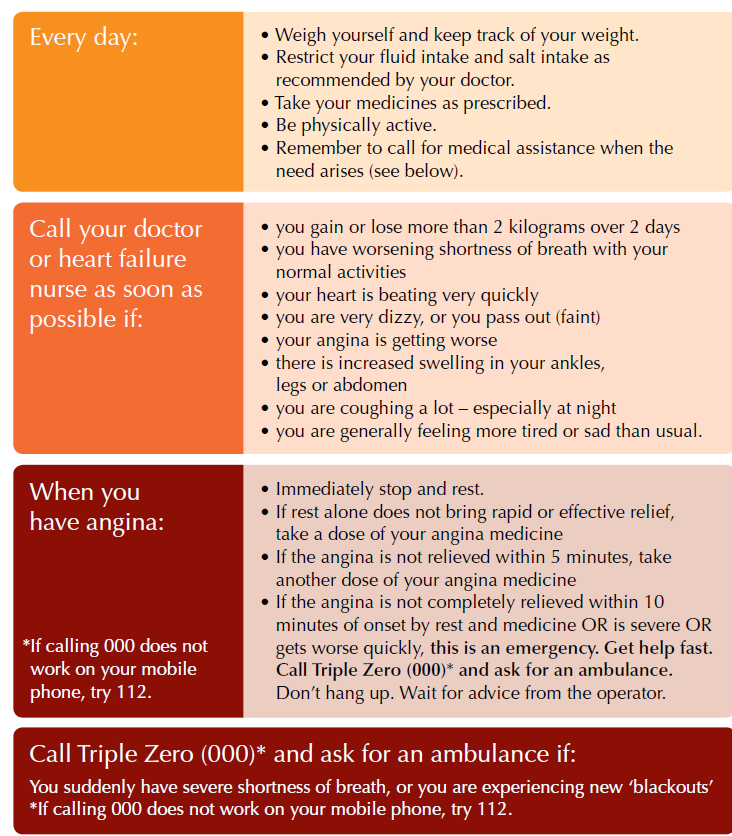
CORONARY HEART FAILURE ACTION PLAN
(from the National Heart Foundation of Australia)
EXERCISE IN CARDIAC REHABILITATION – WHY?
- Inactivity causes 25% of the burden on the body in heart disease.
- Exercise improves fitness and strength
- Exercise reduces blood pressure and improves cardiac blood flow
- Exercise has a number of mechanisms that stabilise formation of plaques prevent progression.
Although there are complex medical conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes and unstable angina where exercise may be contra-indicated it is important to have an exercise programme created by a cardiac rehabilitation therapist (usually a physiotherapist) who can monitor heart rate, blood pressure and other signs when a programme is being carried out.
The main Cardiac Rehab lifestyle parameters if you are at risk of or if you have heart disease are:
- Stop smoking, avoid second hand smoke
- Limit alcohol to low risk levels
- Healthy eating – Saturated fat <7%, Trans-fats <1% daily intake, Limit salt to 1550mg,
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Waist circumference should be less than 94cm for men and less than 80 cm for women.
- Body Mass Index 18.5-24.9kg/m2
- Assessed for depression and social support
- Be PHYSICALLY ACTIVE






